Brief: Step-by-step beginner’s guide to installing TeamViewer on Linux. It also explains how to use TeamViewer on Linux.
TeamViewer is a remote desktop application primarily used to connect to a different system quickly and securely. It lets you remotely connect to someone’s desktop, transfer files, share screen and video conferencing.
It is extremely popular for its simplicity and ease of use. It is mainly used to provide technical support to remote computers.
It’s a cross-platform software available for Windows, Mac OS X, Linux, iOS and Android and there is a web browser support too. Though TeamViewer is a proprietary software, it is available free of charge for non-commercial use and offers almost everything the paid version has to offer.
TeamViewer features
- Allows you to take a remote control of a system.
- Supports video conferencing, group calls, desktop sharing.
- There is a 256 bit AES session encoding and 2048 bit RSA key exchange for a secure connection.
- Wake-on-LAN feature allows switching on your computer remotely.
- Supports rebooting your system or servers while on the go.
- Switching between multiple screens is easy.
Installing TeamViewer in Linux
TeamViewer provides .deb binaries for Debian and Ubuntu-based Linux distributions. It also has .rpm packages for Fedora and SUSE. There is also a tarball for other Linux distributions.
You can grab a copy of TeamViewer from the official download page:
[ms_button style=”2d” link=”https://www.teamviewer.com/en/download/linux/” size=”medium” shape=”” shadow=”no” block=”no” target=”_self” gradient=”no” color=”blue” text_color=”#ffffff” icon=”fa-cloud-download” icon_animation_type=”fadeIn” border_width=”0″ class=”” id=””]Download TeamViewer[/ms_button]
I will be installing TeamViewer on Ubuntu so I downloaded the .deb file. You can use the graphical installer by double-clicking the downloaded package and following the subsequent instructions.
If you face dependency issues, I suggest you try installing it with GDebi package installer.
Alternatively, if you prefer the terminal way, navigate to the download folder and run the below command:
[ms_highlight background_color=”grey” border_radius=”10″ color=”” class=”” id=””]sudo dpkg -i teamviewer*[/ms_highlight]
In case you are notified of installation failure due to missing dependencies, type the below command to complete the installation.
[ms_highlight background_color=”grey” border_radius=”10″ color=”” class=”” id=””]sudo apt-get install -f[/ms_highlight]
Once installed, you can open TeamViewer from the application menu or run it from the console using the command:
[ms_highlight background_color=”grey” border_radius=”10″ color=”” class=”” id=””]teamviewer[/ms_highlight]
How to use TeamViewer on Linux to connect to other systems
Here are a few things you should know about using TeamViewer for remotely connecting to other systems:
- Both host and target systems should have TeamViewer installed.
- Host and target can be any supported operating systems. For example, you can use it to connect to a Windows system from your Linux system.
- By default, each system is given an ID and a 4 digit password that is generated randomly at each start of the application.
- If you are trying to connect to a remote system, you’ll need to know the ID and the password of the target system.
- Similarly, if you are giving someone access to your system, you need to provide them the password and ID of your system to the remote system.
- Both systems must be connected to the internet.
- You are not required to create an account on TeamViewer to use it.
Now that you know a few things, let’s see how to do it:
Step 1
Start TeamViewer on both host and target systems. You’ll see the ID and password of your TeamViewer application on your screen. Similar info will be displayed on the remote system.
This is important information as it will be required to make the remote desktop connection.

Step 2
For connecting to a system, both the host and target machines should have TeamViewer installed. You will need the unique ID and password of the system to which you want to connect to. Open TeamViewer and under the “Remote Control” type in the ID in Partner ID option, and click on “Connect to partner”:

Quite obviously, it will ask you to enter the password of the target system.

Once you enter the correct password and hit Log On, you should be immediately connected to the target system.
Step 3
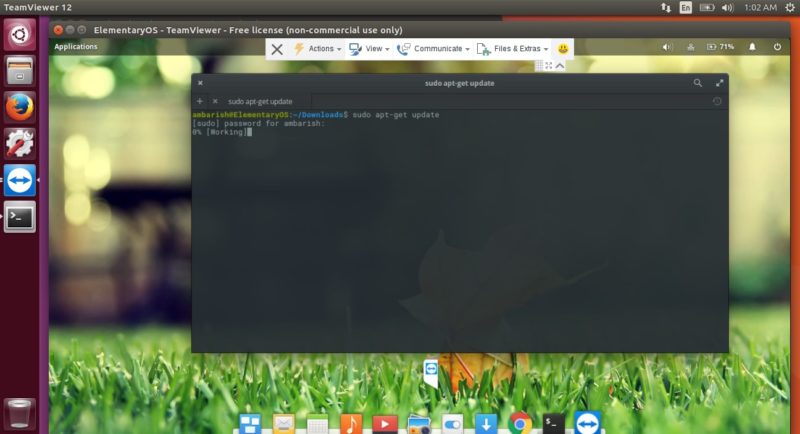
Once connected, you have the full control of the target system. I have a system running Ubuntu from which I established a remote desktop connection to another system running Elementary OS and then I ran a command there!

The top bar provides different options for TeamViewer. Under the Actions tab, you can find options to end the session, reboot your device or even invite additional participants.

View tab contains the most useful options. You can select the screen fit, optimize speed and quality and select the screen resolution for the target system.

Files & Extras gives you the option to take a screenshot or record a session. You can share a file between the two system via drag and drop or using the file manager.

Do more with TeamViewer
There are ways to optimize your TeamViewer experience. Let’s see some of them.
1. Using TeamViewer account for easy access
TeamViewer provides an ID and password which can be used to take control of your system. However, signing up for a free user lets you store these credentials, and quickly connect to a system without the hassle of typing it every time.
2. Recording a session
You can always record a TeamViewer session for a later access or for the records. Once you are connected to TeamViewer, navigate to Extras in the Toolbar and you will find the option to start, pause and stop recording. Once a recording is done, you are prompted to save it.
3. Multiple Sessions support
TeamViewer supports multiple sessions simultaneously, you can take control of a second system without being disconnected from the first one. Click on the + sign in the top left corner to add another machine. For IT support people, this can be very useful.
4. Easy file transfer
You can share a file by selecting File Transfer from the TeamViewer toolbar. You can either select the file which you want to share, or drag and drop a file using option File box. This is important since you can push an application to the target machine and install it without having a physical access.
5. Manage Visual Settings
Visual Settings options lets you optimize your connection to the target machine by giving you options to choose the Quality, Scaling, Screen resolution. It can be accessed via View option. In case there is a lag, you could select Optimize speed under Quality options, or disable GUI animations.
6. Connect with a smartphone
TeamViewer app is available for iOS, Android and Windows 10 Mobile which can help you take a look at your system anywhere, anytime. This lets me access my system and check if some downloads are completed, or even change the music track without reaching out to my system.
I tried taking a control of my system with my Phone and it worked like a charm.

Final Words on TeamViewer
TeamViewer is a great tool when it comes to getting control of someone’s system for troubleshooting or monitoring your own system with your mobile handset. And since it is available for almost every platform, there’s always a way around to help someone by connecting to their system.
Are you a TeamViewer user? What other tools do you use for remote desktop connection in Linux? Let us know in the comments how it helps you!